How to Calculate the Position of a Falling Object
Integrating once more gives d V o T gT 2 2. And Im told to modify the program to compute the position of an object falling for 10 seconds using this formula.

Three Panels Showing Three Graphs The Top Panel Shows A Graph Of Vertical Position In Meters Versus Time In Motion Graphs Graphing Worksheets Physics Lessons
For example if the velocity of the rock is calculated at a height of 810 m above the starting point using the method from Figure when the initial velocity is 130 ms straight up a result of is.

. H t 49 t 2 v 0 t h 0 and then the velocity of the object at a particular time t is given by. Which of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object. Where r is the radius of rotation and v is the perpendicular component of velocity.
Integrating the acceleration once gives V V o g T where V o is the initial velocity presumably zero and T is the time of fall. D 05 g t2. Objects falling faster in the air for example skydivers cause considerable amounts of turbulence and consequently the air resistance experienced by them is much greater.
Where M is the mean anomaly e the eccentricity of the orbit E the eccentric anomaly. V v0 1 2 at. V 0 v 2 v 0 1 2 a t.
M E e sin. For these objects the air resistance is directly proportional to the square of the objects velocity relative. At t 8 s.
In case you want the average V over the fall its half that. Use the formula v u at. Now when the function modeling the pos.
How to Calculate Air Resistance of a Falling Object when the Object Falls Fast in Air. If the air bag stops his fall in 1m then the ratio of the forces will be the inverse of the ratio of the distances. You dont need to calculate the actual Kinetic Energy the body has on impact - just equate the work done by gravity with the work done on the air bag.
The distance fallen after a time of t seconds is given by the formula. V t 98 t v 0. V is the vertical velocity in meterssecond ms or feetsecond fts g is the acceleration due to gravity 98 ms 2 or 32 fts 2 Since the object is moving in the direction of gravity v is a positive number.
Find the absolute value. The energy of a moving object is called kinetic energy and is equal to one half of the objects mass times the square of its velocity. As you can see this is a transcendental function so you will probably need to iterate through a calculator in order to solve it.
Y gt 2 2 v i t See Derivation of Displacement-Time Gravity Equations for details of the derivations Since v i 0 for a dropped object the equation reduces to. V f 98 ms 2 8 s 784 ms. Displacement of a falling object as a function of velocity or time.
V v 0 a t. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Up to 10 cash back If the value of h is in meters and s in meterssec the acceleration due to gravity in meterssec is 49 the equation becomes.
Acceleration due to gravity is 98 msecsec and in. Plug the given time in this example thats t 424 seconds into the function you found in Step 1. Displacement with respect to time.
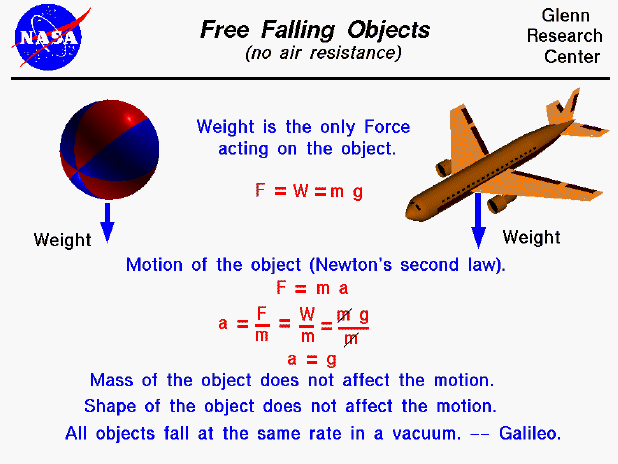
I 1 12mbl2 ml2 4 about the pivot. The general gravity equation for the displacement with respect to time is. For a free falling object the net external force is just the weight of the object.
V v0 at. V v 0 1 2 a t. So taking V o 0 you get T sqrt2dg and Vsqrt2dg.
The distance that a free-falling object has fallen from a position of rest is also dependent upon the time of fall. Since the initial velocity v i 0 for an object that is simply falling the equation reduces to. Adding v0 v 0 to each side of this equation and dividing by 2 gives.
You must solve the Keplers equation. Take the derivative of the function s t t 3 4t. Xt 05 at2 vt x a acceleration -981 ms t time in seconds 10 v initial velocity x initial position.
900 X 30 F air bag X 1 so F air bag 27000N. Li l 2 m2gh. T is the time in seconds.
AAverage acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval. Shae1st finds kinetic energy of a falling object using the kinematic equations to determine velocity and then kinetic energy equation. Position of a falling object Power Function Table 2.
Because we only consider the acceleration due to gravity in this problem the speed of a falling object depends only on its initial speed and its vertical position relative to the starting point. V0 v 2 v0 1 2 at. S t v t v t 3t 2 4 Step 2.
The position of the ball dropped from rest measured at different times Timers Log 1 Log 5 Position y m 088 042 056 157 078 304 104 541 114 650 130 845 144 1057 162 1312 174 200 1514 2000 1. Y gt 2 2. F W Substituting into the second law equation gives.
The final momentum is given by. After the collision the angular velocity of the object and beam is the same. KEfrac12mv2 When thinking about the impact force of a falling object you can calculate the energy of the object at its point of impact if you know the height from which it was dropped.
Where u is the initial velocity if it fell from some height it is taken as zero a is the acceleration due to gravity t is time in seconds and v is the desired velocity after time t. Lf I ω. BAverage acceleration is always equal to the displacement of.
They have a combined moment of inertia of. Since v0 v 2 v v 0 v 2 v for constant acceleration then. LeeH That V Lee gives is the final V.
This distance can be computed by use of a formula. Keywords Learn how to solve particle motion problems. A W m m g m g The acceleration of the object equals the gravitational acceleration.
The mass size and shape of the object are not a factor in describing the motion of the object. Draw a graph of position y as a function of time 1. Her results show that.

Different Equations Of Motion For Free Falling Object Teachoo
No comments for "How to Calculate the Position of a Falling Object"
Post a Comment